This article is one of the four articles written to easily understand the Data Vault architecture. Part one covers the Data Vault overview, Data Vault architecture and the OLTP source that has been used for the Data Vault design.
Please note that the OLTP, Staging, Vault and InfoMart databases developed for this series are all on the Microsoft SQL server, and the integration between different databases is done through SQL queries.
Data Vault overview
Data Vault is one of the database modelling method based on the third normal form. This model separates business keys, descriptive data of these business keys and the relationship between different business keys.
Data Vault’s three main components are:
- Hubs
- Links
- Satellites
Hubs: Hubs hold the business key of an entity. For example, Employee ID in an organization.
Links: Links represent the relationship between different business keys. For example, employees associated with the departments.
Satellites: Hold the descriptive data of the business keys. For example, employee details: employee name, address, email, etc.
Basic structure of the Data Vault’s components is shown below.

Data Vault architecture
Basic three-tier architecture of the Data Vault is as follows:
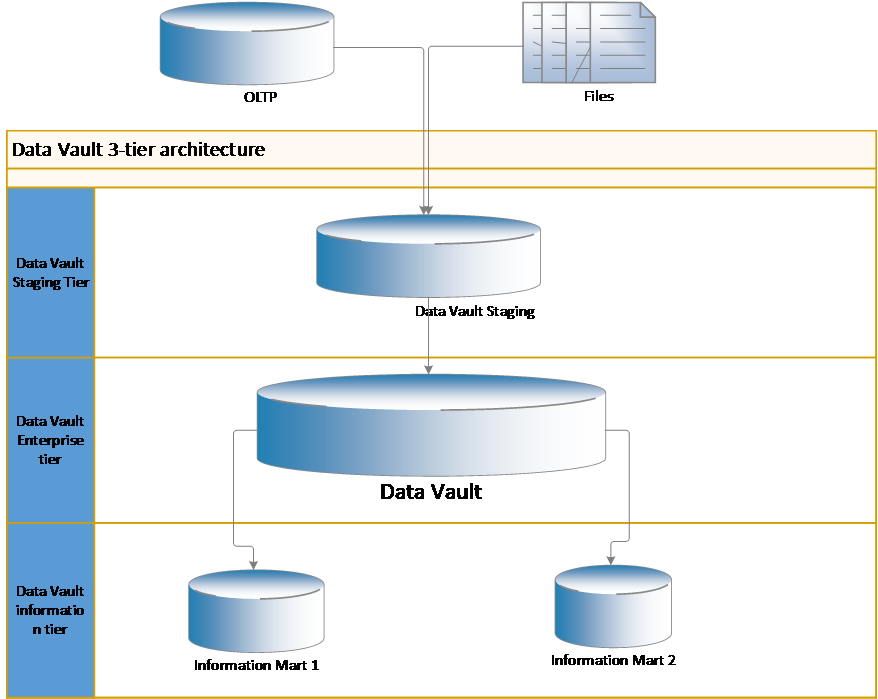
Data Vault Staging
This is the first layer in the Data Vault architecture. Staging area is the temporary area of the data coming from various source systems. Data load process from source systems to the staging area should be made quicker to reduce workloads on the operation systems. Structure of the staging table should be made as a clone of the source table.
A few extra columns in the staging tables are recommended to store the record origin, load time and hash columns for the hash key computations for Data Vault loading.
Data Vault
This is the second layer in the Data Vault architecture. Data stored in this layer is permanent and time-variant. With Hash columns in place, any change to the source data is tracked and recorded at the granularity from the source system. Data Vault layer is also called as Raw Data Vault layer.
Information Mart
This is the third layer in the Data Vault architecture. Data stored in this layer is used by the business users. Data in fed from Data Vault, this layer provides valuable information to the end-users.
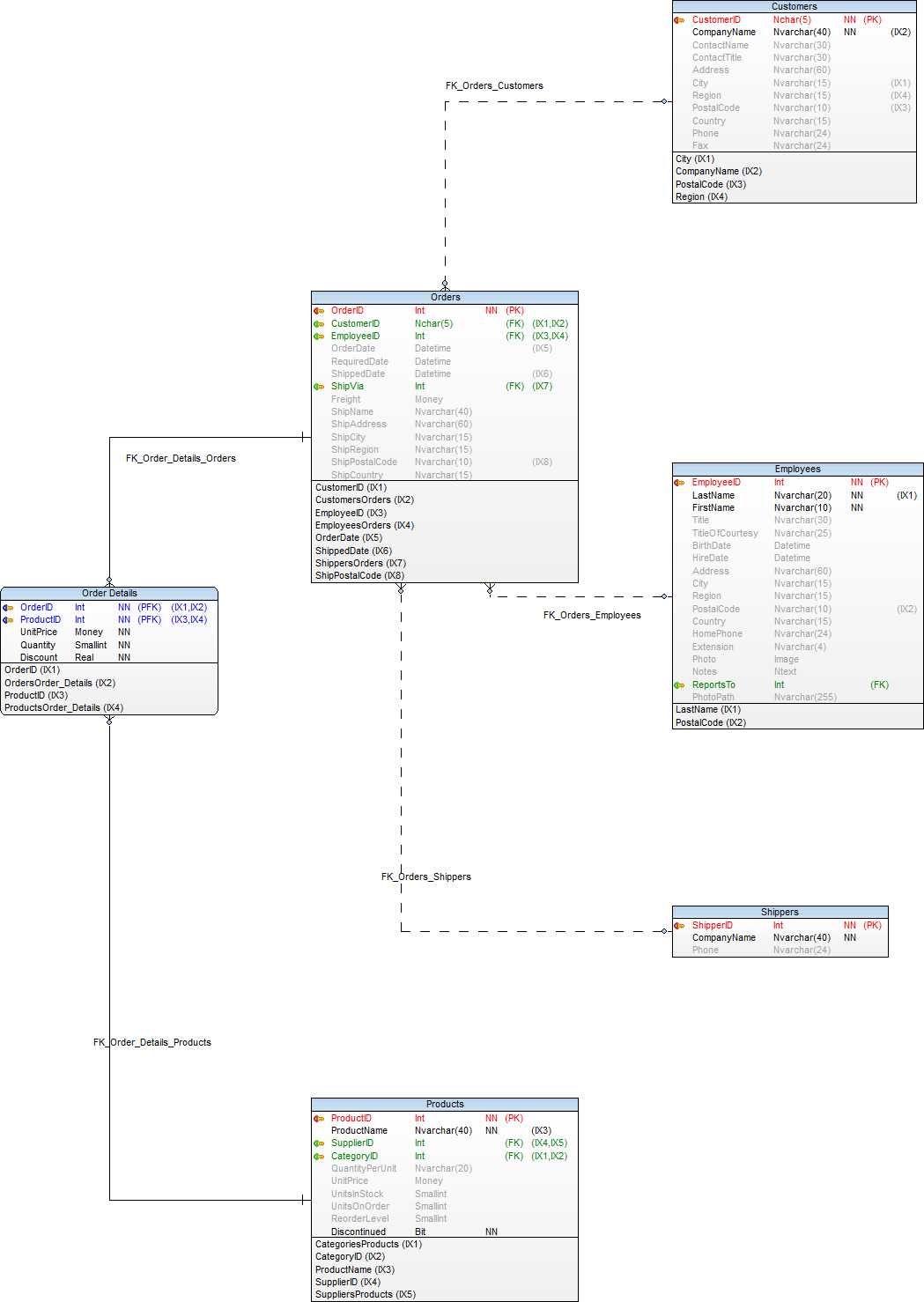
OLTP source used in this series
This concludes the post. In the next article, we will look at the Data Vault staging environment.